Evolución en 12 años de los indicadores de lactancia materna y factores asociados en un Centro de Salud acreditado IHAN
Introducción: La Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS) recomienda la lactancia materna exclusiva 6 meses y la mantenida hasta 2 años o más. Nuestro objetivo es estudiar la evolución de indicadores de lactancia (duración, porcentajes de inicio y mantenimiento hasta los 12 meses) en los últimos 12 años en nuestro centro, acreditado recientemente como Centro de Salud IHAN, y la asociación de estos indicadores con distintos factores: educación maternal, forma de nacimiento (parto vaginal o cesárea) y tipo de maternidad (pública o privada).
Material y métodos: Estudio descriptivo prospectivo de cohorte con 803 lactantes nacidos en dos periodos de tiempo separados 12 años: 2003-2004 y 2015-2016. Datos recogidos por entrevista personal en las revisiones del niño sano.
Resultados: La mediana de duración de la lactancia ha mejorado de forma significativa en el segundo periodo (10 meses) respecto al primero (5 meses; p <0,001); también los porcentajes de lactancia al nacimiento y hasta 12 meses (p <0,05). La asistencia a educación maternal ha sido el factor que se asocia de forma más significativa a estos indicadores en ambos periodos; también el parto vaginal (en el primer periodo) y la maternidad pública (en el segundo). Estos resultados se confirman en el análisis multivariante.
Conclusiones: En estos 12 años se ha producido una mejora significativa en los indicadores de lactancia de nuestro centro. Los factores favorables para iniciar y mantener la lactancia materna son asistir a los cursos de educación maternal (el más importante), nacer por parto vaginal y en maternidad pública.
Proyecto internacional INSPIRE: «¿Qué es normal en la leche humana» (II). Compuestos inmunológicos solubles
La protección inmunológica del recién nacido depende principalmente de factores inmunitarios maternos proporcionados a través de la leche. Sin embargo, muy pocos estudios han evaluado la variabilidad natural de los diferentes compuestos inmunitarios presentes en la leche humana de mujeres sanas pertenecientes a poblaciones heterogéneas. En este contexto, el objetivo de este trabajo fue la detección y cuantificación de una amplia gama de factores inmunitarios solubles, entre los que se incluyen factores de inmunidad innata (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12, INFγ, TNFα) y adquirida (IL-2, IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, IL-17), quimioquinas (IL-8, Groα, MCP1, MIP1β), factores de crecimiento (IL-5, IL-7, EGF, G-CSF, GM-CSF, TGFβ2) e inmunoglobulinas (IgA, IgG, IgM), en la leche producida por mujeres sanas de diversas etnias procedentes de distintos entornos geográficos, dietéticos, socioeconómicos y ambientales. A partir de los resultados de este trabajo, pudimos determinar que un grupo de estos factores (IgA, IgG, IgM, EGF, TGFβ2, IL-7, IL-8, Groα y MIP1β) estaba presente en todas o en la mayoría de las muestras recogidas en todas las cohortes y, por tanto, podría considerarse como el núcleo común (core) de la leche humana en condiciones fisiológicas.
Incidencia y factores de riesgo del dolor durante la lactancia: estudio prospectivo en una consulta de pediatría en atención primaria
Introducción: El dolor durante el amamantamiento destaca entre las principales causas de destete precoz; sin embargo, los estudios acerca de su etiopatogenia son escasos. El objetivo de este trabajo fue analizar la incidencia de dolor durante la lactancia y los factores de riesgo implicados en su aparición.
Pacientes y métodos: Se realizó un estudio observacional longitudinal prospectivo, en el que se incluyeron 63 díadas madre-hijo. Se evaluó la incidencia e intensidad del dolor (Escala Visual Analógica [EVA]) y se valoró de forma sistemática la técnica de lactancia y la presencia de anquiloglosia en el lactante, entre otros factores de riesgo potencialmente implicados en el dolor. También se realizó un análisis microbiológico de la leche materna.
Resultados: Un 65% de las madres lactantes refirió dolor (EVA ≥3) durante más de 1 semana y, entre ellas, el 29% más de 2 meses. La técnica de lactancia y la anquiloglosia no se relacionaron con un mayor riesgo de aparición de dolor. En cambio, un cultivo de leche materna positivo se asoció con un riesgo muy significativo de dolor (p <0,0001). Se aislaron las mismas especies en las muestras de mujeres con dolor y sin dolor (Staphylococcus epidermidis, S. aureus, estreptocos del grupo viridans, Rothia mucilaginosa y Corynebacterium spp.), pero con una concentración significativamente mayor en el primer grupo. No se aisló Candida spp. en ninguna muestra.
Conclusiones: El análisis microbiológico de la leche materna puede ser un aspecto clave para un abordaje del dolor adecuado y efectivo durante la lactancia.
Fórmulas extensivamente hidrolizadas. Importancia del grado de hidrolisis
La importancia de la nutrición en los primeros 1.000 días de la vida
La recomendación de lactancia materna exclusiva hasta los 6 meses de vida: algunas consideraciones
La recomendación global de la Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS) de dar «lactancia exclusivamente materna durante los primeros 6 meses de vida» es considerada por las madres y los profesionales sanitarios un objetivo nutricional idóneo para cualquier lactante, si así se desea y no hay impedimento para efectuarla. Es importante destacar que el llamado «Tercer Mundo», con millones de desfavorecidos, era y es el objetivo fundamental de la difusión y puesta en marcha de un programa de salud de la OMS muy amplio, en el que se incluye dicha recomendación. Las circunstancias socioeconómicas y culturales en los países de nuestro ámbito occidental son diferentes, con una historia bien establecida, por lo que las recomendaciones de la European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition son compatibles con la citada recomendación de la OMS respecto a la introducción de la alimentación complementaria desde los 4 meses. Por ello, esta recomendación debe aplicarse con flexibilidad en nuestro ámbito pediátrico y vigilar los riesgos de ferropenia que puede conllevar.
Frecuentación en urgencias de los neonatos en un área suburbana de Madrid
Factores de riesgo de la mastitis infecciosa durante la lactancia
La mastitis infecciosa es una patología común durante la lactancia y constituye una de las primeras causas de destete precoz. Por tanto, debería considerarse un problema de salud pública relevante, ya que priva a la pareja madre-hijo de los incuestionables beneficios de la lactancia. No obstante, la mastitis humana ha sido hasta la fecha una enfermedad subestimada, ya que su diagnóstico microbiológico no se realiza de forma sistemática, y habitualmente sólo se consideran mastitis los casos agudos que cursan con una sintomatología evidente. En este trabajo se revisa la literatura médica acerca de los posibles factores de riesgo que podrían estar implicados en el desarrollo de mastitis infecciosa, incluidos los aspectos relacionados con el historial médico de la madre y del hijo, el embarazo, el parto, el posparto y la lactancia. En este sentido, el hecho de profundizar en el conocimiento de dichos factores permitirá proporcionar un asesoramiento adecuado durante la lactancia, así como diseñar estrategias para prevenir esta enfermedad, con el objetivo final de que muchas parejas madre-hijo disfruten plenamente de los beneficios que proporciona la lactancia materna.
Deshidratación hipernatrémica asociada a la alimentación con lactancia materna en el periodo neonatal
Consecuencias inesperadas de las iniciativas actuales de lactancia materna / Incidencia de las medicinas alternativas y complementarias en las tasas de vacunación de la gripe en niños estadounidenses
Los efectos adversos de las vacunas están claramente sobrepasados por sus beneficios. Pero, debido a la baja incidencia de estas enfermedades prevenibles gracias a las vacunas, la población puede tener una percepción errónea de que su riesgo es bajo, lo que provoca una participación relativamente baja en el programa de vacunación.
La vacuna de la gripe se recomienda para toda la población mayor de 6 meses, administrada anualmente. En los niños la vacuna es segura, y aunque su efectividad varía cada año, es inmunológicamente eficaz. Sin embargo, la vacunación de la gripe en niños estadounidenses es subóptima y sustancialmente más baja que la de otras vacunas.
El uso de las MAC en los niños no es raro. La estimación nacional de 2007 muestra que casi un 12% de los niños en Estados Unidos ha usado algún tipo de MAC en los últimos 12 meses. Este hecho es más común entre adolescentes, blancos no hispanos, con un alto nivel de educación de sus padres, una situación económica estable y un seguro de salud privado. La literatura disponible sugiere que es menos probable que se vacunen los niños que usan MAC, aunque no se ha estudiado cómo afecta esto a la vacuna de la gripe. El presente estudio examina la asociación de MAC con la vacuna de gripe en una muestra representativa de niños de Estados Unidos.
Se usaron los datos recogidos desde 2012 por el National Health Interview Survey (NHIS), acerca de la salud de la población no institucionalizada de Estados Unidos a través de entrevistas (contestadas por los padres) sobre unos 10.000 niños entre 4 y 17 años. Se estableció como variable dependiente si se habían puesto la vacuna de la gripe en el último año, y como variable independiente si habían utilizado alguna vez, por razones de salud, alguno de los 37 tipos de MAC en los últimos 12 meses. La prevalencia de haber usado alguna vez MAC variaba entre el 0,01 y el 6,4%, excepto el uso de multivitaminas/multiminerales (62,3%).
Los 37 tipos de MAC se agruparon en 4 categorías:
1. Sistemas de medicina alternativa (SMA; p. ej., acupuntura) (3,8%).
2. Terapias de base biológica (TBB; p. ej., suplementos dietéticos) (7,6%).
3. Terapias basadas en el cuerpo y manipulativas (TBCM; p. ej., manipulación quiropráctica) (7,3%).
4. Tratamiento mente-cuerpo (TMC; p. ej., yoga) (5,3%).
El 43% de los niños recibió la vacuna antigripal en los 12 meses previos. Se ponían menos vacunas los sujetos que habían utilizado alguna vez SMA o TBCM, y la tasa más alta de vacunados se observó entre los que habían usado multivitaminas/multiminerales. No había ninguna asociación significativa entre los que habían utilizado alguna vez TBB o TMC. Las tasas de vacunación eran menores en los casos siguientes: niños blancos no hispanos (menor por cada año de edad cumplido), los que no habían efectuado recientemente una revisión del niño sano, los que no tenían una enfermedad crónica grave, los que carecían de seguro médico y los que habían realizado menos visitas médicas recientemente.
Discusión
Aunque las MAC se usan mayoritariamente junto con la medicina convencional, el presente estudio provee una clara evidencia de que los niños de Estados Unidos que alguna vez han usado algún subtipo de TAM o TBCM tenían menores tasas de vacunación contra la gripe. Estos tipos de MAC requieren un contacto con los profesionales que las practican (a diferencia de los suplementos de hierbas, las dietas alternativas o el yoga), críticos respecto a las vacunas, en contra de ellas o que aconsejan calendarios vacunales distintos al recomendado por el gobierno federal.
Varias covariables estaban significativamente asociadas, entre ellas acudir con más frecuencia al pediatra, ser de menor edad o padecer asma. Generalmente, la educación parental más alta se asocia a una mayor tasa de vacunación gripal en niños, aunque en este estudio se encontró una asociación inversa.
La limitación fundamental de este estudio es que se excluyó a los menores de 4 años, el grupo de edad con mayor riesgo de desarrollar complicaciones asociadas a la gripe.
Lo que aporta este trabajo:
Es cada vez mayor el número de personas que usan terapias complementarias y alternativas, algunas veces frente a tratamientos o recomendaciones de la medicina convencional. En este estudio se pone de manifiesto que utilizar alguna de estas terapias (en especial las suministradas por otras personas) se asocia a tasas de vacunación de la gripe en niños inferiores a las del resto de la población. Hoy día la pregunta sobre las terapias alternativas y complementarias debería formar parte de la anamnesis en cualquier consulta médica y explicar que su empleo no debe contradecir datos evidentes como, por ejemplo, la eficacia de la vacunación de la gripe.
Anquiloglosia neonatal. ¿Existe un exceso de indicación intervencionista?
El pediatra y las recomendaciones nutricionales en la mujer embarazada y que lacta
La alimentación y la actividad física antes y durante el embarazo afectan de forma importante a la salud de la madre y de su hijo. Además, el periodo de lactancia acarrea un aumento de las necesidades de energía y nutrientes para la madre. Existe cada vez un mayor número de datos científicos sobre la trascendencia de la alimentación en las primeras etapas de la vida y el riesgo de desarrollar posteriormente enfermedad, que se engloba en la noción de «la nutrición en los mil primeros días». La intervención nutricional preventiva debería comenzar en el periodo periconcepcional, prolongarse durante el embarazo y los primeros años de vida y continuar como un programa de desarrollo de hábitos de vida saludable. Durante estos periodos es preciso que la mujer consiga alcanzar una ingesta suficiente de determinados nutrientes, más que un aumento en el aporte energético total. El pediatra debe considerarse un agente de salud pública clave para mejorar los hábitos de salud de toda la población. Desde el Comité de Nutrición de la Asociación Española de Pediatría se ha considerado de interés que el pediatra conozca las recomendaciones actuales para la alimentación de la mujer embarazada y lactante, con el fin de ejercer su influencia sobre la salud del recién nacido y del lactante.
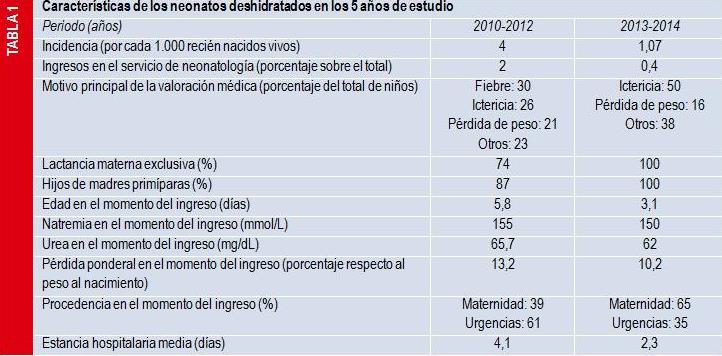
Lactancia materna y deshidratación neonatal. ¿Se puede disminuir el número de casos?
1. Ip S, Chung M, Raman G, Chew P, Magula N, DeVine D, et al. Breastfeeding and maternal and infant health outcomes in developed countries. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007; 153: 1-186.
2. Agostoni C, Braegger C, Decsi T, Kolacek S, Koletzko B, et al; ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. Breast-feeding: a commentary by the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009; 49: 112-125.
3. Melissa Bartick, Arnold Reinhold. The Burden of suboptimal breastfeeding in the United States: a pediatric cost analysis. Pediatrics. 2010; 125: e1048-e1046. Disponible en: http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/125/5/e1048.full.pdf
4. Unal S, Arhan E, Kara N, Uncu N, Aliefendioğlu D. Breast-feeding-associated hypernatremia: retrospective analysis of 169 term newborns. Pediatr Int. 2008; 50(1): 29-34.
5. Peñalver Giner O, Gisbert Mestre J, Casero Soriano J, Bernal Ferrer A, Oltra Benavent M, Tomás Vila M. Deshidratación hipernatrémica asociada a lactancia materna. An Pediatr (Barc). 2004; 61(4): 340-343.
6. Boskabadi H, Maamouri G, Ebrahimi M, Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Esmaeily H, Sahebkar A, et al. Neonatal hypernatremia and dehydration in infants receiving inadequate breastfeeding. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2010; 19(3): 301-307.
7. Pelleboer RA, Bontemps ST, Verkerk PH, Van Dommelen P, Pereira RR, Van Wouwe JP. A nationwide study on hospital admissions due to dehydration in exclusively breastfed infants in the Netherlands: its incidence, clinical characteristics, treatment and outcome. Acta Paediatr. 2009; 98(5): 807-811.
8. Aguayo Maldonado J, Arana Cañada Argüelles C, Arena Ansótegui J, Canduela Martínez V, Flores Antón M, Gómez Papí A, et al. IHAN Calidad en la asistencia profesional al nacimiento y la lactancia. Informes, estudios e investigación. Madrid: Ministerio de Sanidad, Política e Igualdad. Centro de publicaciones, 2011.
Factores ambientales relacionados con la duración de la lactancia: estudio de seguimiento a 1 año
Factores asociados al inicio de la lactancia materna y razones de la madre para la toma de su decisión
Introducción: Los beneficios de la lactancia materna (LM) son bien conocidos. En estudios previos se constata que aproximadamente un 20% de las madres deciden no iniciarla. Existe un escaso conocimiento de los factores que predicen tal decisión y los motivos maternos para ello. En este estudio analizamos la prevalencia de inicio de la LM, los factores asociados y las razones maternas al respecto.
Método: Estudio de prevalencia de inicio de la LM de gestaciones ≥36 semanas. Recogida de variables mediante encuestas presenciales en las primeras 24 horas posparto. Estudio multivariante de los factores asociados al inicio de la LM.
Resultados: Se estudió un total de 452 pares, madre-recién nacido. El 81% inició la LM. Los factores favorecedores fueron la opinión favorable de la pareja (odds ratio [OR]= 28,49; intervalo de confianza [IC] del 95%: 5,34-151,95), la opinión neutral de la abuela materna (OR= 4,79; IC del 95%: 0,99-23,76), haber dado LM al hijo previo (OR= 22,63; IC del 95%: 5,68-90,07) y residir en la misma provincia donde está ubicado el hospital (OR= 47,34; IC del 95%: 16,09-139,31). Los factores desfavorecedores fueron: el hábito tabáquico de la madre (OR= 0,37; IC del 95%: 0,15-0,92), haber tenido abortos previos (OR= 0,35; IC del 95%: 0,20-0,60) y precisar tratamiento farmacológico al iniciar la lactancia (OR= 0,25; IC del 95%: 0,08-0,74).
Conclusiones: Aportamos ciertos factores conocidos y otros novedosos asociados al inicio de la LM y los motivos de la madre para la toma de su decisión. Los tratamientos farmacológicos maternos son un factor asociado para no iniciar la LM, corregible con un asesoramiento adecuado. Urge adoptar medidas correctoras para conseguir tasas de inicio de la LM cercanas al 100%. Es necesaria la unificación de criterios respecto a lo que se considera «inicio de la LM» para comparar resultados de futuras investigaciones.
Factores de riesgo de la mastitis infecciosa en mujeres lactantes: estudio de casos y controles en población española (parte 2)
Objetivo: El objetivo de este estudio fue identificar los posibles factores de riesgo asociados a la mastitis infecciosa en mujeres lactantes.
Métodos: Se diseñó un estudio de casos y controles, con 368 casos (mujeres lactantes con mastitis) y 148 controles (mujeres lactantes sin mastitis). La información se recogió de forma retrospectiva mediante encuestas, que recopilaron información sobre diversos aspectos del historial médico de la madre y del hijo, así como distintos factores relacionados con el embarazo, el parto, el posparto y la lactancia que pudieran estar implicados en el desarrollo de la mastitis. La asociación entre la mastitis y dichos factores se realizó mediante un análisis bivariante y un modelo de regresión logística multivariante.
Resultados: Los resultados del análisis multivariante pusieron de manifiesto que los principales factores relacionados con un incremento estadísticamente significativo del riesgo de padecer mastitis fueron los siguientes: presencia de grietas en los pezones (p <0,0001), uso de antibióticos orales (p <0,0001), bombas de extracción (p <0,0001) y antifúngicos tópicos (p= 0,0009) durante la lactancia, padecimiento de mastitis en lactancias previas (p= 0,0014), subida de la leche después de 24 horas posparto (p= 0,0016), antecedentes familiares de mastitis (p= 0,0028), separación madre-hijo tras el parto durante más de 24 horas (p= 0,0027), aplicación de pomadas en los pezones (p= 0,0228) e infecciones de garganta (p= 0,0224).
Conclusiones: En este trabajo se han identificado diversos factores de riesgo relacionados con el desarrollo de la mastitis infecciosa. Este conocimiento permitirá proporcionar un asesoramiento adecuado durante la lactancia sobre los factores de riesgo modificables, como el uso de bombas de extracción o de una medicación inadecuada. También se podría identificar antes del parto a las mujeres con un riesgo elevado de desarrollar mastitis, como las que presentan antecedentes familiares de dicha enfermedad, y por tanto desarrollar estrategias para su prevención.
Episodio aparentemente letal neonatal precoz
El contacto «piel con piel» tras el nacimiento ha demostrado efectos beneficiosos sobre la adaptación a la vida extrauterina y el vínculo madre-hijo, así como sobre la frecuencia y la duración de la lactancia materna. Teniendo en cuenta que la mayoría de los episodios aparentemente letales neonatales precoces se producen en las primeras 2 horas de vida, durante el contacto piel con piel, creemos imprescindible garantizar la vigilancia en ese periodo.
Factores de riesgo de la mastitis infecciosa en mujeres lactantes: estudio de casos y controles en población española (parte 1)
Objetivo: El objetivo de este estudio fue identificar los posibles factores de riesgo asociados a la mastitis infecciosa en mujeres lactantes.
Métodos: Se diseñó un estudio de casos y controles, con 368 casos (mujeres lactantes con mastitis) y 148 controles (mujeres lactantes sin mastitis). La información se recogió de forma retrospectiva mediante encuestas, que recopilaron información sobre diversos aspectos del historial médico de la madre y del hijo, así como distintos factores relacionados con el embarazo, el parto, el posparto y la lactancia que pudieran estar implicados en el desarrollo de la mastitis. La asociación entre la mastitis y dichos factores se realizó mediante un análisis bivariante y un modelo de regresión logística multivariante.
Resultados: Los resultados del análisis multivariante pusieron de manifiesto que los principales factores relacionados con un incremento estadísticamente significativo del riesgo de padecer mastitis fueron los siguientes: presencia de grietas en los pezones (p <0,0001), uso de antibióticos orales (p <0,0001), bombas de extracción (p <0,0001) y antifúngicos tópicos (p= 0,0009) durante la lactancia, padecimiento de mastitis en lactancias previas (p= 0,0014), subida de la leche después de 24 horas posparto (p= 0,0016), antecedentes familiares de mastitis (p= 0,0028), separación madre-hijo tras el parto durante más de 24 horas (p= 0,0027), aplicación de pomadas en los pezones (p= 0,0228) e infecciones de garganta (p= 0,0224).
Conclusiones: En este trabajo se han identificado diversos factores de riesgo relacionados con el desarrollo de la mastitis infecciosa. Este conocimiento permitirá proporcionar un asesoramiento adecuado durante la lactancia sobre los factores de riesgo modificables, como el uso de bombas de extracción o de una medicación inadecuada. También se podría identificar antes del parto a las mujeres con un riesgo elevado de desarrollar mastitis, como las que presentan antecedentes familiares de dicha enfermedad, y por tanto desarrollar estrategias para su prevención.
Tetania neonatal por hipocalcemia secundaria a hipovitaminosis D. Forma extrema de una enfermedad que resurge
Desde el inicio de la era industrial, el raquitismo ha sido una enfermedad endémica. Con el
descubrimiento de la vitamina D y el aporte de suplementos, sobre todo en las fórmulas lácteas infantiles,
prácticamente había desaparecido, pero durante los últimos años parece haberse convertido de nuevo en
un problema de salud pública. La carencia de vitamina D se asocia no sólo a problemas óseos, sino
también a un importante incremento del riesgo de enfermedades cardiovasculares, autoinmunes,
infecciosas y tumorales.
Comunicamos un caso de tetania neonatal por hipocalcemia secundaria a hipovitaminosis D en un
neonato de menos de 2 días de vida. La precocidad de la aparición y la gravedad clínica son
excepcionales. Además, advierte del problema emergente que constituye el déficit de vitamina D y de la
necesidad de instaurar la suplementación con ésta vitamina, siguiendo las últimas recomendaciones de la
Asociación Española de Pediatría.
Alimentación complementaria dirigida por el bebé («baby-led weaning»). ¿Es una aproximación válida a la introducción de nuevos alimentos en el lactante?
Tradicionalmente, la introducción de la alimentación complementaria pasa por un periodo de alimentación triturada, hasta que el lactante adquiere las habilidades para tomar comida en trocitos. En la práctica, el momento de la introducción de alimentos no triturados se ha ido retrasando, lo que ha llevado a una mayor frecuencia de problemas en la alimentación en esa edad.
La alimentación complementaria guiada por el bebé (baby-led weaning) se basa en que sea el propio lactante quien se alimenta llevándose la comida a la boca, en vez de ser alimentado con una cuchara por un adulto. En esta práctica, el lactante se incorpora pronto a la comida familiar y comparte su menú, manteniendo la lactancia materna. Algunos estudios observacionales de pequeño tamaño sugieren que esta técnica favorece los patrones de alimentación, aunque no se ha podido demostrar si se plasma en efectos beneficiosos para la salud. Su difusión surge a raíz de la recomendación de la Organización Mundial de la Salud de retrasar la introducción de la alimentación complementaria hasta los 6 meses, en un momento en que el lactante ha alcanzado hitos importantes en su desarrollo, lo que haría posible que se alimentara por sí mismo. Algunos de los aspectos contenidos en esta filosofía serían válidos para la mayoría de los lactantes, aunque es difícil aceptarlo en su radicalidad (oposición a las comidas con cuchara).
Las principales dudas que se plantean respecto a esta técnica son saber si el lactante recibe suficiente variedad de nutrientes y en una cuantía suficiente (p. ej., el hierro), si existe riesgo de atragantamiento y si la técnica es aplicable en todos los niños.
A fecha de hoy, parece importante que los pediatras conozcamos en qué consiste esta técnica de alimentación y podamos responder a las preguntas de los padres sobre su eficacia y seguridad.
Papel de los cereales en la alimentación infantil
En el primer año de vida, la lactancia materna es el referente durante al menos los 6 primeros meses, pero hay una cierta dispersión de tendencias cuando se llega a la edad de introducir la alimentación complementaria. Tradicionalmente, los cereales han sido y son los primeros alimentos que se aconsejan como inicio de la alimentación complementaria. En los últimos tiempos se ha observado un descenso que posiblemente esté relacionado con algunos tópicos negativos, por lo que nos ha parecido oportuno actualizar su papel.
Las características fisiológicas de los primeros años de vida son circunstancias que tienen gran importancia para conseguir una buena adaptación en la progresión de la alimentación atendiendo a las capacidades que el nuevo ser va adquiriendo en estos primeros años, preferentemente en sus funciones digestivas, renales y neuromusculares.
Los cereales son una excelente fuente nutricional, pero no todos tienen las mismas propiedades, por lo que se repasa su composición para valorar los beneficios que representan en la salud del niño, tanto como aporte de la energía que va necesitando para cubrir sus necesidades, como para evitar deficiencias proteicas y de vitaminas y oligoelementos. No sólo es importante la cantidad, sino también la calidad y el contexto de una alimentación variada y equilibrada que ayude a compensar el resto de los aportes.
Ya que los cereales son fundamentales en la alimentación de nuestros hijos, es bueno recordar algunas recomendaciones actualizadas sobre su uso en los diferentes periodos de la vida, ya sea en forma de papillas en los primeros meses o de cereales más complejos en etapas más avanzadas, así como resaltar la vigencia que conservan en la alimentación de los primeros años si se utilizan correctamente.
Novedades en la alimentación complementaria para recién nacidos con lactancia materna
Introducción: La leche materna debería ser el alimento exclusivo de los bebés hasta los 6 meses, pero puede ser necesaria la alimentación complementaria entre los 4 y los 6 meses.
Objetivo: Valoración clínica del empleo de una nueva papilla de cereales preparada con agua, en niños de 4 meses de edad con lactancia materna.
Material y métodos: Fueron reclutados 30 lactantes sanos, con lactancia materna hasta los 6 meses. A los 4 meses se indicó durante 4 semanas una toma diaria de dichos cereales en sustitución de una toma de leche materna. La composición, preparada al 25% con agua, aporta 106 kcal/100 g. El promedio de ingesta de papilla fue de 190 kcal/día. Se constató una diferencia significativa en el Z-score (p <0,01) para el peso a los 4 meses de 0,15 ± 0,88 frente al peso a los 5 meses de 0,40 ± 0,85. Las curvas de talla y perímetro craneal fueron normales. No se alteró el ritmo deposicional y la aceptación de la papilla fue excelente.
Conclusión: El nuevo preparado es una magnífica alternativa para iniciar la alimentación complementaria en lactantes con lactancia materna exclusiva que precisen el inicio de dicha alimentación sin incorporar fórmula.
Influencia de la oxitocina administrada durante el parto en el mantenimiento de la lactancia materna. Estudio preliminar
Introducción: El uso de la oxitocina (Oxt) durante el parto está tan generalizado que hay una tendencia a asumir que sus efectos son bien conocidos. El objetivo del presente estudio es determinar si la Oxt administrada durante el parto posee alguna influencia sobre el mantenimiento de la lactancia materna exclusiva (LME).
Pacientes y métodos: Este trabajo forma parte de un estudio cuyo objetivo principal es valorar la influencia de la Oxt administrada durante el parto en los reflejos neonatales primitivos. Se trata de un estudio descriptivo observacional realizado en 20 díadas madre-hijo. Se incluyeron madres primigestas que no habían presentado complicaciones durante el embarazo y habían tenido un recién nacido a término sano fruto de un parto vaginal inducido o estimulado con Oxt. Se realizó una llamada telefónica a los 3 meses.
Resultados: Las dosis de Oxt que recibieron durante el parto las madres que no mantenían LME al cabo de 1 y 3 meses fueron superiores a las que mantenían LME (p <0,05).
Conclusión: La Oxt administrada durante el parto puede influir de forma negativa en el mantenimiento de la LME.
Lactancia materna y mastitis. Tratamiento empírico basado en la sintomatología y los agentes etiológicos
Las mastitis representan la principal causa médica de destete precoz. Generalmente, las mastitis agudas se diagnostican sin dificultad, pero no así las mastitis subagudas o las subclínicas.
Prevalencia de la lactancia materna en el sector de salud del Hospital «Son LLàtzer» de Palma de Mallorca
Objetivo: Conocer la incidencia y la prevalencia de la lactancia materna (LM) en los 6 primeros meses de vida, y relacionarla con las variables que predisponen al inicio de la lactancia y su mantenimiento, las dificultades más frecuentes y los motivos de abandono y/o la introducción temprana de otros alimentos. Se pretende comparar las prácticas hospitalarias recomendadas por la Organización Mundial de la Salud y la prevalencia de lactancia materna al inicio.
Material y método: Estudio descriptivo transversal con recogida de datos retrospectivos, mediante encuesta telefónica a madres de bebés de 15, 30, 90 y 180 días, y los registros de enfermería de la maternidad sobre alimentación de los recién nacidos.
Resultados: La prevalencia de la decisión de lactancia materna en el momento del parto es del 81,2%, y al alta del hospital del 76%. Va descendiendo progresivamente, y a los 15 días de vida es del 73,6%, al mes del 72,5%, a los 3 meses del 56,9%, y a los 6 meses del 37,8%. Las madres que han hecho «piel con piel» después del parto y han iniciado la lactancia precoz en la primera hora tienen una mayor prevalencia de lactancia materna completa frente a lactancia parcial a los 15 días (un 86,6 y un 86,3%, frente un 56,3 y un 55%, respectivamente). La asociación desaparece a partir del primer mes, y tampoco se observa ninguna relación entre la práctica de «piel con piel» y la lactancia materna en la primera hora, con el abandono precoz de la lactancia. La edad de la madre no se asocia al tipo de la lactancia, según los datos obtenidos. El 79,3% de las madres con estudios universitarios mantiene la lactancia hasta los 3 meses, frente al 62,2% de las madres con otros estudios; a los 6 meses, todas lo hacen de forma similar.
Los momentos críticos de abandono se presentan alrededor del primer mes, y entre el cuarto y quinto mes de vida.
Los motivos de lactancia parcial durante el primer mes son principalmente (75,64%) el llanto, el hambre, la poca ganancia de peso y la leche insuficiente. Los motivos de lactancia parcial entre los 3 y 6 meses son la recomendación profesional (60,6%), motivos de trabajo o estudios (18,2%), y leche insuficiente, llanto o hambre (18,2%).
Conclusiones: Las tasas de lactancia materna en el sector de salud del Hospital «Son Llàtzer» son similares a las obtenidas en otros estudios y a las de la Encuesta Nacional de Salud de 2006. Las prácticas hospitalarias adecuadas mejoran la prevalencia de la lactancia al inicio; después son muchos los factores que intervienen. Para mejorar la prevalencia de la lactancia los meses posteriores, se debe mejorar la atención sanitaria tras la hospitalización y las medidas institucionales que la protejan.
Factores etiopatogénicos del asma bronquial en la edad infantil
Introducción: Hay muchos factores implicados en el desarrollo y la progresión del asma bronquial infantil.
Objetivo: Valorar si estos factores están claramente implicados en la etiopatogenia de esta enfermedad.
Material y métodos: Revisión bibliográfica estructurada de los trabajos sobre factores de riesgo para el asma publicados en la bibliografía biomédica actualizada durante los últimos 5 años.
Resultados: Se han seleccionado 14 artículos que aportan datos a favor y en contra sobre los factores considerados de riesgo para el desarrollo y la progresión del asma bronquial, como la genética o los antecedentes familiares, la atopia, las anomalías de la función pulmonar, el sexo, la lactancia materna y los estilos de alimentación, el tabaco, las infecciones respiratorias virales y otros factores ambientales (hipótesis de la higiene).
Conclusiones: Hay discordancia entre la implicación de los diferentes factores etiopatogénicos del asma con la propia enfermedad.
Evaluación de un programa de intervención para incrementar el inicio y la duración de la lactancia materna en un centro de salud*
Objetivos: Evaluar un programa de intervención para promocionar la lactancia materna llevado a cabo en el Centro de Salud de Nazaret (Valencia) desde 1997 y que consiste en repartir y explicar un tríptico diseñado para este fin.
Material y métodos: Se recogieron datos demográficos, antropométricos y respecto a la alimentación infantil en el grupo de recién nacidos antes de la intervención (1995 y 1996) (grupo 1) y en el grupo de nacidos después de la intervención (de 1998 al 2000, ambos inclusive) (grupo 2).
Resultados: En el grupo 1, comenzaron la lactancia materna el 52,4%, y en el grupo 2 el 56%. La duración media de la lactancia materna, para aquellos que la empezaron, fue para el grupo 1 de 3,53 meses (IC del 95%, 3,25-3,77), y para el grupo 2 de 3,78 meses (IC del 95%, 3,31-4,25), con un log rank test de 1,21 (p no significativa). No hubo diferencias respecto al motivo por el que no se inició la lactancia materna o por el que se abandonó. La edad de la madre, estado civil o número de hijos anteriores no tuvieron efecto sobre el inicio o el mantenimiento de la lactancia materna tras la intervención.
Conclusiones: El programa de intervención no supuso un cambio relevante en el inicio ni en el mantenimiento de la lactancia materna.
Medicamentos, plantas, tóxicos, enfermedades y lactancia: una ayuda en español en Internet (www.e-lactancia.org)
Los beneficios de la lactancia materna, para el niño y la madre, su familia, el sistema sanitario y la sociedad en general, están muy bien documentados en múltiples publicaciones. Suprimir una lactancia sin un motivo de peso es una grave irresponsabilidad desde el punto de vista sanitario. Más del 90% de las mujeres pueden tener que tomar medicamentos o productos de fitoterapia durante el periodo de lactancia, lo que constituye un motivo clásico de cese de la lactancia, pese a no estar demostrado su peligro real más que en un pequeñísimo porcentaje de productos: fenindiona, amiodarona, derivados del ergot, antineoplásicos, yoduros y psicodrogas de abuso. Del mismo modo, sólo 6 enfermedades de la madre contraindican o hacen prácticamente imposible la lactancia. Con sentido común, unos conocimientos básicos de farmacología y pediatría y buenas guías (libros, revistas y páginas web), podemos asesorar a las mujeres que lactan, deben tomar remedios para alguna dolencia o sufren una enfermedad. Las madres huirán de informaciones erróneas, basadas sólo en prejuicios o en el Vademécum. Una página web (www.e-lactancia.org), en español y de sencillo manejo, nos ayudará a tomar decisiones acertadas ante más de 1.400 opciones diferentes implicadas en la lactancia materna.
Lactancia materna dolorosa: estrategias de tratamiento para el pediatra
El dolor y los problemas del pecho son habituales en las madres que amamantan: originan importantes molestias, disminuyen la confianza de las madres en su capacidad para amamantar y, con frecuencia, son causa de abandonos precoces. A menudo, los profesionales no conocemos el mejor modo de prevenir o tratar estos problemas, ya que su abordaje no suele estar incluido en los programas de formación de pregrado o posgrado. Con esta revisión, los autores pretenden ofrecer al profesional que atiende a la díada madre-hijo una herramienta básica basada en los conocimientos más actuales sobre el tema.
Programas de intervención para promocionar la lactancia materna. Proyecto PALMA
La lactancia materna (LM) es la mejor forma de alimentar al recién nacido y al lactante, ya que confiere una serie de beneficios tanto a corto como a largo plazo. Según recomienda la Organización Mundial de la Salud, la LM debe mantenerse durante los primeros 6 meses como alimento exclusivo, y a partir de este momento junto con la alimentación complementaria, mientras la madre y el niño deseen. Según los datos disponibles, el tiempo medio de mantenimiento de la LM en nuestro entorno no supera los 3-5 meses, el abandono precoz durante el primer mes de vida ocurre en un 30% de los casos y sólo en un 10-20% se mantiene a los 6 meses. Se revisan los factores de riesgo para la instauración y el mantenimiento de la LM, los momentos clave para la promoción de la LM desde las instituciones sanitarias y el tipo de medidas que son más efectivas. Asimismo, se presenta el Proyecto PALMA, que pretende evaluar la efectividad de un programa de intervención de apoyo multidisciplinario a la LM desde atención primaria en un grupo de lactantes frente a un grupo control.
Proctocolitis hemorrágica en lactante exclusivamente alimentado al pecho
La lactancia materna es la forma ideal de alimentación del recién nacido. Entre sus múltiples ventajas está la de prevenir las enfermedades alérgicas. La colitis hemorrágica es una forma de intolerancia a las proteínas de leche de vaca, cuya frecuencia está aumentando especialmente en los niños lactados al pecho. Se debe pensar en ella en un lactante con hebras de sangre en heces sin afectación del estado general, en el que se ha descartado la existencia de una fisura anal y una infección gastrointestinal. El diagnóstico se basa fundamentalmente en la respuesta clínica a la dieta de exclusión. El diagnóstico de certeza raramente se obtiene, ya que el buen pronóstico y la buena evolución del cuadro hacen innecesarios los estudios invasivos. Sólo en casos de persistencia del sangrado se debe valorar la realización de una endoscopia con toma de biopsias. Su tratamiento es la dieta exenta de proteínas de leche de vaca. El tratamiento de los niños alimentados con fórmula es sencillo. Sin embargo, en los casos de lactancia materna exclusiva hay algunos interrogantes que permanecen sin aclarar.
El método de la madre canguro
Desde hace tiempo, las unidades de neonatología están tratando de introducir los cuidados centrados en el desarrollo, que pretenden mejorar el desarrollo del prematuro a través de intervenciones especiales, entendiendo al recién nacido y a su familia como una unidad. En estos cuidados se incluye el método de la madre canguro (MMC), que se define como el contacto piel con piel entre la madre y el niño prematuro de la forma más precoz, continua y prolongada posible con lactancia materna, para que ambos se beneficien de sus ventajas. El MMC debería ofrecerse a todos los niños prematuros o recién nacidos a término enfermos como una alternativa al cuidado en la incubadora, dado que es efectivo para el control de la temperatura, reduce el riesgo de infecciones y de episodios de apnea, favorece la lactancia materna, permite y fortalece la vinculación madre/padre-hijo, devuelve a los padres el protagonismo del cuidado de sus hijos y reduce la estancia hospitalaria.
Oligosacáridos en la leche humana
La leche materna contiene más de 130 oligosacáridos distintos, que constituyen el tercer componente de ésta. Su concentración total disminuye a medida que avanza el curso de lactancia, de modo que al año contiene menos de la mitad que en las primeras semanas de vida. Los oligosacáridos más abundantes en la leche humana son libres (no conjugados) y neutros y contienen fucosa. Los oligosacáridos fucosilados pueden tener un enlace 2-fucosa o 3-fucosa, composición que varía según la procedencia de las madres y el curso de la lactancia. Los oligosacáridos actúan como receptores competitivos sobre la superficie celular del huésped, previniendo así la adherencia de determinados patógenos. La fracción de oligosacáridos no digerida en la leche materna estimula el crecimiento de bifidobacterias en el colon, y esta flora podría tener efectos beneficiosos de protección frente a infecciones entéricas. Así, los oligosacáridos son un componente principal del sistema inmunológico innato por el cual la madre protege a su hijo de patógenos (entéricos o de otra localización) durante la lactancia.
La lactancia materna en nuestro medio: análisis de la situación
Objetivo: Conocer la prevalencia de la lactancia materna (LM) en nuestro medio y valorar la eficacia de un programa de promoción en el inicio y mantenimiento de ésta.
Método: Estudio descriptivo, retrospectivo mediante la revisión de historias clínicas de los recién nacidos en el año 2005 en nuestra área de salud.
Resultados y conclusiones: Baja prevalencia y duración de la lactancia en función de las recomendaciones de la Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS). La influencia del programa de promoción de LM es escasa.
Tendencia y evolución de la lactancia materna en el norte de Lugo
Introducción: La lactancia materna exclusiva es el mejor método de alimentación del niño durante los 6 primeros meses, y la recomiendan la mayoría de los organismos e instituciones. Pero las tasas de inicio y su duración son todavía muy bajas y variables.
Material y métodos: Se entrevistó tras el parto a las madres que dieron a luz en el hospital durante los años 2001-2003 para conocer el método elegido de alimentación del niño. Se siguió durante el primer semestre de vida a las que amamantaban al alta para conocer la duración de la lactancia y el motivo fundamental de abandono.
Resultados: De 1.166 madres (1.185 recién nacidos vivos), el 69,9% tenía intención de amamantar. De 1.170 niños estudiados, el 31,5% recibió siempre leche artificial; del resto, el 17,4% abandonó la lactancia en la primera semana, el 3,8% entre las semanas 1 y 4, el 12,7% entre las semanas 4 y 12, el 20,8% entre las semanas 12 y 24, y el 13,8% siguió la lactancia tras la semana 24. Las causas fundamentales de abandono fueron: fallo de la técnica de amamantamiento (45,2%), abandono natural (22,1%), trabajo (11%) y enfermedades maternas (8,6%). En las primeras 4 semanas la causa fundamental de abandono es la mala técnica (el 58,1 frente al 41,3%), seguido de enfermedades maternas (el 17,4 frente al 6%) y enfermedades del niño (el 9,8 frente al 2,4%).
Conclusiones: La lactancia materna es un método de alimentación sujeto a muchos factores externos, que se podrían modificar con una educación adecuada de las madres y su entorno, así como con la puesta en marcha de medidas institucionales que la protejan.
Lactancia materna en la Región de Murcia. ¿Seguimos con el problema?
Objetivo: Conocer la prevalencia y la duración de la lactancia materna (LM) en la Región de Murcia.
Método: Estudio transversal (junio de 2007), mediante encuestas a madres de niños menores de 24 meses realizadas en centros de vacunación. El ámbito de estudio estuvo comprendido por 77 zonas de salud de 6 áreas sanitarias de la región, y el muestreo fue proporcional al número de niños nacidos en el área. Se recogieron datos sociosanitarios del niño, de la madre y de la alimentación del niño. Se calculó la prevalencia de LM según las categorías definidas por la Organización Mundial de Salud (OMS) y se estudiaron los motivos de no iniciar y de abandonar la LM.
Resultados: Se obtuvieron datos de 1.836 niños, con una tasa de respuesta del 95,2%. Al alta del hospital, un total de 1.643 niños (89,7%) fueron alimentados con LM; de éstos, el 76,7% (n= 1.405) lo hicieron sin suplementos nutritivos. Al tercer mes mantenían la LM completa el 44,4% y al sexto mes el 36,3%. La mediana de duración de LM exclusiva fue de 75 días y para la LM parcial de 129 días. Los motivos de no alimentar con LM fueron: enfermedad/ingreso (46,7%), falta de leche (28,6%) y decisión de la madre (19,3%). Entre las causas de abandono, cabe citar las siguientes: hipogalactia e insaciabilidad (29,3%) y escasa ganancia de peso (11%). Las variables que mostraron una asociación estadísticamente significativa (p <0,05) con la LM fueron el peso del niño, el tipo de parto y el área sanitaria, y, en relación con la madre, la edad, la paridad, la actividad laboral, el lugar de procedencia y el nivel de estudios.
Conclusiones: Las cifras de LM en la Región de Murcia son similares a las de nuestro entorno, pero se alejan de las recomendadas por la OMS.
Exanguinotransfusión. Experiencia de un hospital de tercer nivel
Introducción: Un porcentaje de recién nacidos (RN) a término sanos desarrollan ictericia clínica en la primera semana de vida. El objetivo principal del tratamiento es evitar la aparición de encefalopatía. La tendencia actual al alta precoz en las plantas de maternidad se ha relacionado con un aumento de la incidencia de hiperbilirrubinemia, que requiere tratamiento intensivo. La exanguinotransfusión (ET) es una técnica que, aunque invasiva, permite disminuir rápidamente la concentración de bilirrubina y minimizar el riesgo de daño neurológico.
Propósito y objetivos: Conocer las características clínicas y epidemiológicas de los RN que requieren ET y las complicaciones derivadas de la técnica.
Material y métodos: Estudio retrospectivo de las historias clínicas de los RN ≥35 semanas y de ≤28 días de vida que ingresaron en la Unidad de Neonatología del Hospital Universitario «Reina Sofía» de Córdoba en los últimos 6 años y que requirieron la realización de ET. Se analizaron las siguientes variables: edad gestacional media, sexo, etiología de la ictericia, tipo de lactancia, horas de vida en el momento de la técnica, concentración máxima de bilirrubina sérica, y necesidad o no de repetición. Además, se revisaron las complicaciones asociadas a la técnica y la necesidad de su repetición.
Resultados: Se diagnosticaron 16 RN con hiperbilirrubinemia extrema que requirieron ET. La etiología más frecuente fue la isoinmunización ABO (56,25%), seguida de la enfermedad por Rh (37,5%). No se encontraron diferencias en cuanto al sexo. Un 68,75% eran alimentados con lactancia materna exclusiva. El promedio de estancia hospitalaria fue de 7 días. El efecto adverso más frecuente fue la trombocitopenia. En un caso se detectó un aumento del trabajo respiratorio y bradicardia. No se diagnosticó ningún caso de convulsiones, kerníctero, sepsis o parada cardiaca. En un caso se produjo perforación intestinal puntiforme con buena evolución posterior. Las otoemisiones acústicas y la ecografía cerebral fueron normales en todos los casos. En 2 RN con isoinmunización Rh fue necesario repetir la ET.
Conclusiones: La mayoría de las reacciones adversas relacionadas con la técnica son alteraciones hematológicas, asintomáticas y tratables.
Guía de orientación para la salud bucal en los primeros años de vida
Introducción: La caries es actualmente la enfermedad infecciosa más frecuente en la infancia, y puede ocasionar graves problemas de salud general. Los diferentes factores etiológicos implicados pueden estar condicionados por los profesionales que asisten al niño y su entorno, especialmente por el pediatra, que es el profesional que tiene el primer y mayor contacto con el bebé y su familia. Por ello, creemos que es indispensable la elaboración de una guía integral con el objetivo de uniformar los criterios y orientaciones para la salud bucal en la primera infancia, y así proveer una información única y efectiva a los padres de nuestros pacientes.
Objetivo: Proponer una guía de salud bucal para los padres, que debe estar consensuada por todos los profesionales que trabajen con niños. De esta forma, los padres tendrán más seguridad sobre el cuidado de sus hijos si poseen la misma información de los diferentes profesionales. Se plantean temas como la lactancia materna, el uso del biberón y del chupete, la transmisión bacteriana precoz, los alimentos con potencial cariogénico, la higiene bucal, el uso de flúor y la primera visita al odontopediatra.
Conclusión: Esta guía de salud bucal para los primeros años de vida fue elaborada con el fin de esclarecer y definir algunos temas en común respecto a la salud bucal, que creemos indispensable en la práctica diaria de los pediatras para reducir las consecuencias físicas, psicológicas, económicas y emocionales que ocasiona la caries en la primera infancia.
Medidas preventivas de los problemas del sueño desde el nacimiento hasta la adolescencia
El sueño es una necesidad fisiológica fundamental para nuestra salud. La infancia es la etapa en la que el sueño adquiere mayor relevancia porque el niño pasa la mayor parte del día durmiendo. El sueño, como toda conducta humana, es susceptible de cierta modificación para aprender a dormir bien. Y este proceso debe ser adaptativo, porque el sueño de los bebés y de los niños se encuentra sometido a una lenta maduración. Para ello, es fundamental que los padres tengan un conocimiento profundo de los patrones del sueño del bebé, del niño y del adolescente. En los niños, la clave está en establecer rutinas, proporcionando al menor los denominados «objetos de transición», que facilitan la asociación del entorno al sueño y fomentan su capacidad de conciliar y mantener el sueño de forma autónoma. En los adolescentes, mantener una disciplina respecto al sueño, restringiendo el uso de los ordenadores y el móvil por la noche, son medidas útiles para mejorar el sueño.
Alimentación complementaria: ¿es igual el perfil nutricional de un puré casero que el de un tarrito comercial?
A partir de los 4-6 meses, la lactancia materna no es suficiente para cubrir las necesidades nutricionales del niño, por lo que se deben introducir alimentos suplementarios para aportar los nutrientes y energía que la leche o fórmulas infantiles no pueden proporcionar. Así, a partir de los 5-6 meses de edad, se comienzan a introducir alimentos sólidos de forma progresiva. Entre este tipo de alimentos, los purés comerciales listos para el consumo han cobrado una gran importancia, debido, entre otros factores, al escaso tiempo del que disponen muchas familias para elaborar purés de forma casera. Dada la poca información de la que se dispone en la actualidad, este estudio ha comparado el perfil nutricional de tres tipos diferentes de purés a base de carne de cordero, ternera y pollo, seleccionando para ello tres marcas comerciales diferentes y elaborando purés caseros para compararlos. Se llegó a la conclusión de que tanto los purés caseros como los comerciales presentan un perfil nutricional muy similar y dentro de los rangos recomendados, con una mayor variabilidad en el contenido proteico y de sodio; en el caso de purés caseros, existe la posibilidad de que la adición de sal pueda llevar a sobrepasar los niveles de sodio recomendados.
Actividad de un banco de leche humana implantado en una unidad neonatal
La leche materna, por sus múltiples beneficios sobre la salud incluso a largo plazo, es reconocida como el alimento de elección para todos los lactantes. En las situaciones en que no se dispone de leche de madre propia, la leche de madre donada es una alternativa válida. Con la finalidad de proporcionar leche humana donada existen bancos de leche humana (BLH) ampliamente distribuidos en todo el mundo y con presencia creciente en nuestro país. Se describe la actividad realizada por el BLH del Hospital «La Fe», integrado en el Servicio de Neonatología con participación de la Unidad de Nutrición, en sus primeros 9 meses de actividad.